Can I Allocate 16gb on Sd for Windows 7 to Increase Performance
No matter how high the operation of your computer, sooner or later it will start to boring downwardly as newer programs enervating faster hardware prove up on your desktop. Chances are performance demands will exceed your computer's capabilities earlier you or your company is ready to pop for a replacement computer. This chapter will help yous make the hardware changes -- large or small -- you need to get the well-nigh work and useful life out of your computer. We'll discuss how to upgrade and install hardware, add a 2nd monitor, connect new and erstwhile hard drives, and add retention.
The unmarried most helpful thing yous can practice to make your Windows 7 computer run at tiptop speed is to give it enough system retention (or RAM, short for random access retentiveness). Merely as a reminder, your calculator uses two types of retentiveness: hd infinite and RAM. RAM holds Windows and the programs you're really using, and Windows vii wants more than RAM than Windows XP, but is happy with what works for Vista (if non fifty-fifty slightly less). As discussed in the early on chapters of this book, Windows 7 can run with as little every bit 512MB of RAM and an 800MHz CPU, merely it will run a flake slowly, and you'll find the experience somewhat unpleasant. Memory is inexpensive these days, and boosting your RAM to at to the lowest degree 1GB volition brand a huge departure. I discuss adding RAM and upgrading CPUs afterward in this chapter.
At present, if you're already running Windows 7 on a full-bore, land-of-the-art system, and your computer has a fast video accelerator, a couple of gigs of fast memory, and fast SATA disks, in that location isn't much more you can do to optimize its hardware. You might just adjust the page file sizes and certainly convert all your partitions to NTFS (which tip is a requirement for Windows 7), or yous might add a ReadyBoost device (more on this after in this affiliate). Some of the settings you tin can make are discussed in Chapter 22, "Windows Management and Maintenance;" Chapter 23, "Tweaking and Customizing Windows;" and Affiliate 24, "Managing Hard Disks."
By the aforementioned token, if y'all're doing common, everyday tasks such as discussion processing, and you're already satisfied with the operation of your computer as a whole, you probably don't demand to worry about performance boosters. Your arrangement is probably running but fine, and the time you lot'd spend trying to fine-tune it might exist improve spent doing whatever it is you use your reckoner for (like earning a living).
If you're anywhere between these two extremes, still, you may desire to look at the tune-ups and hardware upgrades we'll talk over in this chapter.
TIP
This chapter just scratches the surface of the ins and outs of hardware installation and updates. If y'all desire all the details, and I mean all the details, get a copy of the acknowledged book Upgrading and Repairing PCs, by Scott Mueller, published by Que.
ReadyBoost
Microsoft introduced ReadyBoost as part of Windows Vista. Essentially, it immune users to allocate all or function of any unmarried USB flash drive (which Microsoft abbreviates as UFD) or a Secure Digital (SD, SDHC, or mini-SD) memory carte du jour as an extension to cache memory available in organization RAM. In Windows 7 several notable changes are introduced, including
• Vista limited ReadyBoost space to a maximum of 4GB (which is all that 32-fleck operating systems tin handle anyway) for both 32- and 64-bit versions. In Windows 7, 64-bit versions tin allocate up to 128GB for a ReadyBoost enshroud.
• Vista express eligible memory devices to UFDs and SD cards; Windows 7 works with those devices plus Meaty Flash (CF), all forms of MemoryStick (MS, MS Duo, MS Pro, and so on), and most other memory cards as well. As with Vista versions, devices must come across minimum speed requirements (12.eight Mbps read/write speeds) for use as ReadyBoost cache devices.
• Vista limited ReadyBoost to a single memory device; in Windows vii you can allocate ReadyBoost cache on multiple memory devices at the aforementioned time. When spread beyond multiple devices functioning might not be equally fast as when ReadyBoost cache comes from a single device, still.
To allocate infinite on a retentivity device for ReadyBoost, right-click the drive icon in Windows Explorer, and so click the ReadyBoost tab in its Backdrop dialog box. Figure 27.one shows two different UFDs in utilise on an x64 Windows 7 machine; the Backdrop dialog box on the left comes from an NTFS-formatted UFD (NTFS or exFAT are required to create a ReadyBoost enshroud file greater than 4GB in size), while the box on the right is from a FAT-32 formatted UFD (mixing and matching works fine).
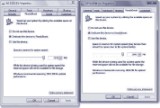
Effigy 27.ane
In Windows seven, ReadyBoost enshroud works with multiple devices, where not all formats demand be identical.
BIOS Settings
Windows 7 depends on proper BIOS settings to enable it to find and use hardware correctly. At a minimum, your drives should be properly configured in the system BIOS, and your CPU type and speed should be properly fix (either in the BIOS or on the motherboard, depending on the arrangement). Thanks to some clever work by Microsoft's engineers, Windows seven boots faster than other 32-bit versions of Windows, but you lot can improve kicking speed further with these tips:
• Prepare your BIOS boot lodge to start with drive C: and then that you can skip the floppy stepper motor test.
• Disable floppy drive seek.
• Turn off any Quick Power-On Self Tests. Some BIOSs have such an option that enables a quicker bootup by skipping some of the internal diagnostics that would usually take place on startup. It makes bootup faster simply also leaves you susceptible to errors; some problems volition non be detected at startup.
Altered BIOS Settings Forbid Estimator from Booting
Today's calculator BIOSs include enough cabalistic settings that it's possible to alter ane in a way that prevents proper booting. Before you mess with advanced CMOS settings (not just simple things such as time, date, boot order, power settings, ports, and so on), read the manual for the computer or motherboard. If you decide to change anything, tape the sometime value before making the change. When in doubt, don't alter advanced CMOS settings that affect how the chipset works, whether and where BIOS and video shadowing is used, and and so on. By pattern, default settings from the motherboard maker work under well-nigh situations and OSs. Because Windows is the most popular PC Os, you lot tin can bet it has been tested and configured for Windows 9x, NT, 2000, XP, Vista, or Windows 7 (unless your motherboard is very old).
That said, what practise y'all do if you've changed something in the CMOS and the estimator won't boot? You lot tin attempt the computer'southward or motherboard's manual or website for information about Windows vii settings. If you discover aught, reset all settings to their factory defaults. Most CMOS setups have a Set to Default or like command yous can issue. This should become you out of nigh whatever jam.
Using the Set to Default choice might too exist a good grade to take if you make CMOS settings that prevent your figurer from booting and yous can't remember how to disengage those changes. Default settings are normally conservative enough to work under almost circumstances. The BIOS in some systems may also have a Neglect-Condom Defaults option that sets your BIOS to its most conservative settings.
If what you've done has changed the hard deejay Type, or if you manually entered the number of sectors, tracks, platters, and and then on, and at present it won't kick, use the Auto Detect Hard Disk BIOS setting to discover and enter those numbers automatically. (This is known every bit drive autotyping.)
Upgrading Your Hard Deejay
One of the most constructive improvements you tin make to a organization is to get a faster or larger hard drive, or add another bulldoze. SCSI difficult disks used to seriously one-up IDE drives, but the new brood of Ultra DMA EIDE drives (which I call One-time MacDonald Disks -- EIEIO!) and Series ATA (SATA) drives are speedy and much cheaper than SCSI. An EIDE passenger vehicle supports four drives (two each on the chief and secondary channels) and is almost always built in to your motherboard. Adding an optical (usually a DVD±RW or a Blu-ray) drive claims i, leaving y'all with a maximum of 3 EIDE hard drives unless yous install a separate addition EIDE host adapter or have a motherboard with RAID support. The EIDE spec tops out at 133MBps. SATA supports 1 drive per aqueduct, simply the latest SATA II systems can reach top transfer speeds of 300MBps. Because optical drives likewise come with SATA connections these days, many new systems skip EIDE in favor of SATA.
TIP
Many recent motherboards feature onboard IDE and even SATA RAID, which can perform either mirroring (which makes an immediate backup re-create of one drive to some other) or striping (which treats both drives as part of a single drive for speed). Although the RAID features on these motherboards don't support RAID 5, the safest (and most expensive!) class of RAID, they work well and are much less expensive than whatever SCSI form of RAID. Just remember that mirroring gives you extra reliability at the expense of speed because everything has to exist written twice, and striping with only ii disks gives you actress speed at the expense of reliability -- if one hard disk fails, you lose everything. You lot can at present discover external terabyte boxes with multiple drives in them that can exist ready for striping or mirroring (RAID 0 or ane) at amazingly affordable prices.
The post-obit are some essential considerations for upgrading your difficult disk arrangement:
• Don't put a hard drive and an optical bulldoze on the same aqueduct unless you must. (Put the hard drive on the main IDE1 aqueduct and the optical drive on the secondary IDE2 channel.) On some computers, the IDE channel negotiates downwards to the slowest device on a channel, slowing down a hard disk drive'southward effective transfer rate. Be sure that the hard bulldoze containing Windows is designated equally the Master Master bulldoze.
• Defragment the hard disk with the Defragmenter utility, which y'all can reach through Computer. Right-click the drive, select Backdrop, Tools tab, Defragment Now. Practice this every week (or run Defrag and prepare upwardly a schedule so it runs weekly), and the process volition accept just a few minutes. Only, if you lot wait months before you try this the beginning time, be prepared to wait a long time for your system to terminate. You lot can also buy third-political party defragmenting programs that do a more thorough job. For more about defragmenting, see Affiliate 24.
• Get a faster disk drive (and maybe controller if necessary to support the bulldoze): Upgrade from standard Parallel ATA (PATA) to SATA drives if possible. If y'all take slower (4,200or five,400RPM) drives, upgrade to quicker ones such equally the increasingly popular 7,200RPM or 10,000RPM drives. The faster spin rate bumps up system operation more than yous might expect. Buy drives with as large a cache buffer as yous can afford. Drive technology is quickly outdated, so practice some web reading before purchase.
Adding RAM
Mayhap the most price-effective upgrade you can make to any Windows-based organisation is to add RAM. This 1 is a no-brainer: If your disk pauses and thrashes each fourth dimension you lot switch betwixt running applications or documents, you need more than RAM. Although Microsoft says Windows vii can run with as piddling as 512MB of RAM, we institute that this results in barely acceptable behavior. At to the lowest degree Microsoft was realistic about information technology this time effectually. Microsoft had claimed XP could run with 64MB, but that was a stretch. Running with 64MB caused intolerably deadening performance. Windows 7's published minimum is 512MB, but if you run memory-intensive applications and want decent operation, you'll want to upwards information technology to 1GB, if not 2.
Windows automatically recognizes newly added RAM and adapts internal settings, such equally when to swap to deejay, to take best advantage of any RAM you throw its way. Upgrade to at least 1GB of RAM if you can afford information technology, especially if your arrangement uses the economical synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM) or double-data-charge per unit (DDR) SDRAM dual in-line retention modules (DIMMs). Memory prices fluctuate constantly, merely these days 2GB DIMMs sell for about $25. This is a cost-effective upgrade indeed. But be certain to get the correct memory for your motherboard. A huge variety of memory technologies are out there. At the time this was written, common technologies included SDRAM, Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), DDR, DDR2, and DDR3. Retentiveness speeds range from 100MHz (labeled PC100) to 2200MHz (labeled DDR3-2200). Also, there are error-correction code (ECC) and non-error-correcting RAM varieties (desktop and notebook PCs use non-ECC RAM).
TIP
For more nearly RAM developments and technology, go to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_access_memory.
To find out what type of memory y'all need, check with your calculator manufacturer or the transmission that came with your computer or motherboard. Get the fastest compatible memory that your CPU can employ and that your motherboard supports. You can get RAM that'south rated faster than you currently need, but you won't gain any speed reward -- just a greater likelihood of beingness able to reuse the memory if yous later upgrade your motherboard. Hither's a website with some adept data about RAM and even possibly what kind your computer uses: www.pcbuyerbeware.co.united kingdom of great britain and northern ireland/RAM.htm.
The maximum amount of RAM you can use depends on your calculator's hardware and the version of Windows 7 you are using. The following table lists the version and maximum amounts. Many terminal-generation computers cannot use more than than 4GB of memory, and that's all that 32-bit versions of Windows can address, even if you lot could plug it in without a BIOS upgrade. Check with the computer or motherboard manufacturer's data sheets or website to effigy out whether y'all take to flash upgrade the system board BIOS to support more than 4GB of RAM.
Version: All 32-bit Windows 7 versions; RAM Maximum: 4GB
Version: 64-flake Home Basic; RAM Maximum: 8GB
Version: 64-flake Habitation Premium; RAM Maximum: 16GB
Version: 64-fleck all other versions; RAM Maximum: 128GB+
TIP
Microsoft has changed its nomenclature with Windows 7. What used to be called the Windows Compatibility List or Hardware Compatibility Listing (too abbreviated HCL) is now called the Windows Logo'd Products Listing. If you want to make life easy for yourself, before you purchase hardware for your Windows seven organisation, bank check thelists on the Microsoft site (look for Windows 7 items at https://winqual.microsoft.com/hcl/default.aspx. Or when looking on a box in a store or online, it should have a "Certified for Windows seven" or "Windows vii" logo on information technology.
![]()
![]() Installing and replacing Windows 7 hardware
Installing and replacing Windows 7 hardware ![]() Upgrading to Windows seven hardware for maximum functioning
Upgrading to Windows seven hardware for maximum functioning![]() Adding and removing Windows seven hardware
Adding and removing Windows seven hardware![]() Installing and troubleshooting multiple monitors for Windows seven
Installing and troubleshooting multiple monitors for Windows seven![]() Installing, configuring and testing a UPS for Windows vii
Installing, configuring and testing a UPS for Windows vii![]() How Windows seven hardware upgrades affect licensing
How Windows seven hardware upgrades affect licensing
Printed with permission from Que Publishing. Copyright 2009. Windows 7 In Depth by Robert Cowart and Brian Knittel. For more information about this title and other similar books, please visit Que Publishing.
Dig Deeper on Desktop management, sales and installation
-

7 major server hardware components you should know
-

Cache vs. RAM: Differences between the two memory types
-

11 tips to improve Windows 10 functioning
-

Flash memory vs. RAM: What'due south the divergence?
normantordely1965.blogspot.com
Source: https://searchitchannel.techtarget.com/feature/Upgrading-to-Windows-7-hardware-for-maximum-performance



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Can I Allocate 16gb on Sd for Windows 7 to Increase Performance"
Posting Komentar